As enterprises continue to scale and digitize operations, the need for high-performing backend systems becomes increasingly critical. This case study highlights the modernization of a large energy platform, focusing on the migration from Ruby on Rails to a reactive Java architecture, along with improvements in API design and overall performance.
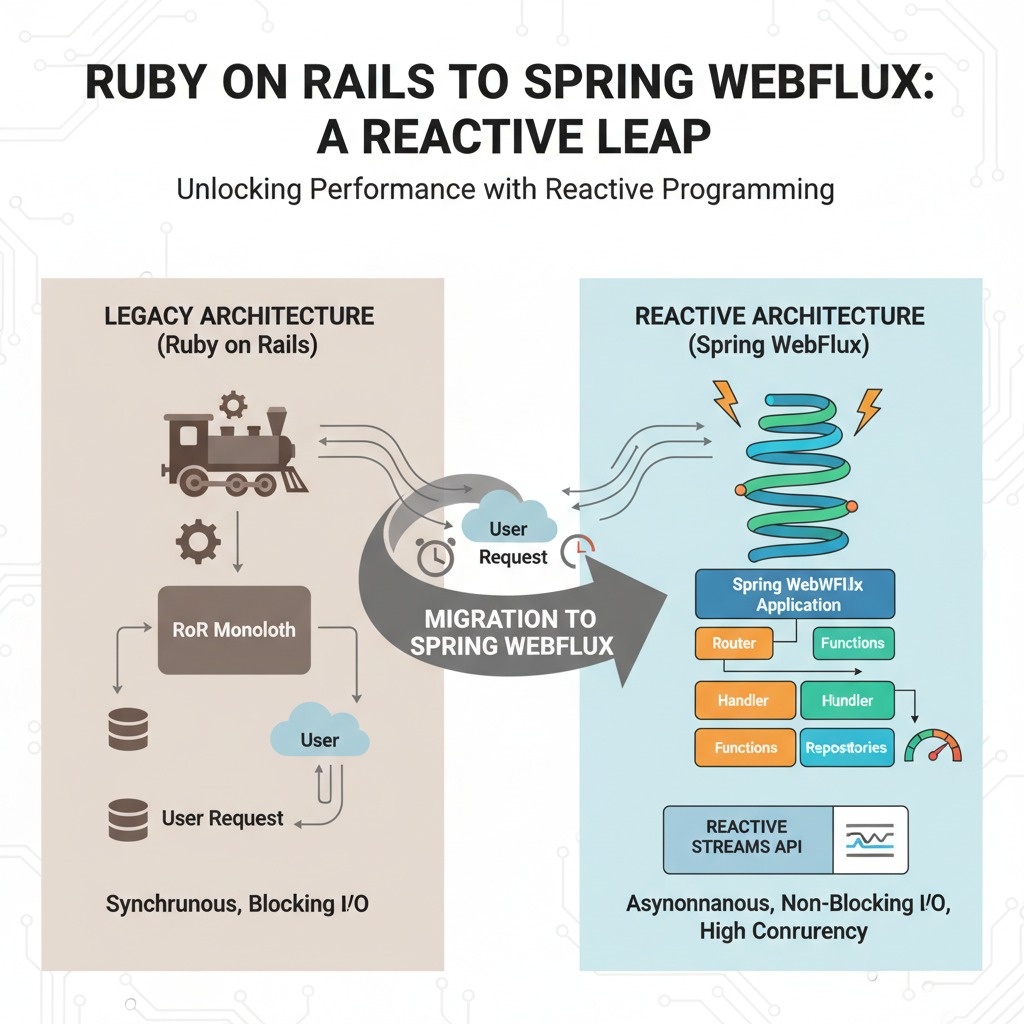
Migration from Ruby on Rails to Java Spring WebFlux
The project began with a clear objective: transition critical backend services from a monolithic Ruby on Rails (RoR) system to a more scalable and performant solution.
The client’s RoR services were reliable but limited under heavy load. To address these challenges, the team selected Java Spring WebFlux, a reactive programming framework built on Project Reactor.
Why WebFlux?
- Non-blocking, asynchronous processing
- Better suited for high concurrency
- Ideal for data streaming and real-time workloads
Key Benefits Post-Migration
- Faster request handling and response times
- Improved scalability under peak load
- Lower resource consumption per request
This shift enabled the platform to handle significantly higher traffic while maintaining reliability.
Real-Time Hardware Issue Resolution
In addition to software migration, the project addressed real-time hardware issues detected by RoR-based services. These often stemmed from inaccurate or delayed data from inverters, meters, and gateways.
The engineering team applied root cause analysis using system logs and telemetry. Handlers were updated to bypass or correct faulty data without disrupting operations. This ensured data accuracy across dashboards and analytics systems.
Graceful Error Handling: Legacy vs Reactive
In the legacy system, device failures often triggered generic 500 errors. WebFlux introduced structured error recovery.
Ruby on Rails (Rescue Block)
def fetch_data
begin
data = DeviceDataService.new.fetch(params[:id])
render json: data
rescue StandardError => e
render json: { error: e.message }, status: 500
end
end
WebFlux (Reactive Error Handling)
public Mono<ServerResponse> getDeviceData(ServerRequest request) {
String deviceId = request.pathVariable("id");
return deviceService.fetchData(deviceId)
.onErrorResume(ex -> {
log.warn("Error fetching data: {}", ex.getMessage());
return Mono.just(new DeviceData("default", 0.0));
})
.flatMap(data -> ServerResponse.ok().bodyValue(data));
}
Why it’s better: Even if the device fails, the system responds gracefully with fallback logic.
Real-Time Data Streaming with WebFlux
The shift also enabled true real-time data streaming, replacing the old polling-based method.
Rails (Static Fetching)
def stream_data
meter = Meter.find(params[:id])
data = meter.readings.last(100)
render json: data
end
WebFlux (Reactive Streaming)
@GetMapping(value = "/meters/{id}/stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<MeterReading> streamMeterData(@PathVariable String id) {
return meterService.streamReadings(id);
}
public Flux<MeterReading> streamReadings(String meterId) {
return Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.flatMap(tick -> meterRepository.fetchLatestReading(meterId))
.filter(Objects::nonNull);
}
Why it’s better: Instead of snapshots, continuous data flows allow live monitoring.
Unified Site Creation API
Previously, more than 16 internal apps managed their own site-creation APIs, causing fragmentation. A unified Site Creation API consolidated these into one reusable, standardized process.
Legacy vs Reactive Code
Ruby on Rails (Controller-Based API)
class SitesController < ApplicationController
def create
site = Site.new(site_params)
if site.save
render json: site, status: :created
else
render json: { errors: site.errors.full_messages }, status: :unprocessable_entity
end
end
private
def site_params
params.require(:site).permit(:name, :location, :customer_id)
end
end
WebFlux (Handler-Based Reactive API)
public Mono<ServerResponse> createSite(ServerRequest request) {
return request.bodyToMono(Site.class)
.flatMap(siteService::createSite)
.flatMap(savedSite -> ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).bodyValue(savedSite))
.onErrorResume(error -> ServerResponse
.status(HttpStatus.UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY)
.bodyValue(Map.of("error", error.getMessage())));
}
@Configuration
public class SiteRouter {
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route(SiteHandler handler) {
return RouterFunctions.route(POST("/api/sites"), handler::createSite);
}
}
Why it’s better: The reactive version decouples logic, enables non-blocking execution, and handles errors more gracefully — critical for stability at scale.
Benefits of the Unified API
- Reduced code duplication across services
- Easier onboarding and maintenance
- Standardized validation and registration logic
- Backward compatibility for phased rollout
Performance Reporting and System Optimization
A detailed report measured migration impact on:
- Throughput and latency
- Data transmission rates
- CPU and memory usage
Performance-critical modules were rewritten in WebFlux, delivering near real-time energy data to customers.
Code-Level Takeaways
This modernization reflects a broader move from blocking, monolithic designs to modular, reactive architectures.
Key Gains
- Non-blocking request handling
- Real-time data streaming
- Robust error management
Conclusion
This project shows how a phased modernization strategy can improve performance, stability, and scalability. By combining reactive programming, API consolidation, and real-time diagnostics, the platform was future-proofed for global energy demands.
👉 For more insights, explore The Road to Reactive Spring Cloud or visit the official Spring WebFlux documentation.
Our Recent Blogs
https://www.codecrafttech.com/resources/highlights/enho-application-optimization.html


 Banking
Banking
 Healthcare
Healthcare
 Energy
Energy
 Manufacturing
Manufacturing
 Education
Education
 Highlights
Highlights
 Blogs
Blogs
 Whitepapers
Whitepapers